Solar water pumps present a clean, simple and energy-efficient alternative to traditional electric and fuel-driven pump sets. They are part of an environmentally friendly approach in agriculture and can be used to exploit every region, whether its developed or poor.
Due to their immense potential for productive use and agricultural productivity, solar water pumps are now powering more and more agriculture projects. Knowing that 40% of the global population relies on agriculture as its main source of income, access to water remains an ongoing struggle for many people. This is what solar aims to change and introduce a cost-effective future for around 500 million small-scale farmers all around the world.
The main components in a solar pumping system include a photovoltaic (PV) array, an electric motor and a pump. Solar water pumping systems, on the other hand, are classified as either direct current (DC) or alternating current (AC) systems based on their motor’s ability. Recently, the concept of brushless DC (BLDC) motors for solar pumping water applications was presented as well.
Classification and types of solar pumps
When it comes to stand-alone solar powered water pump systems, the main types include rotating and positive displacement pumps. Centrifugal pumps are the common choice for rotation and are designed for fixed head applications. Their output increases in proportion to their speed of rotation.
Additionally, pumps are also classified as submersible and surface pumps, based on their placement (underwater and above the waterline).
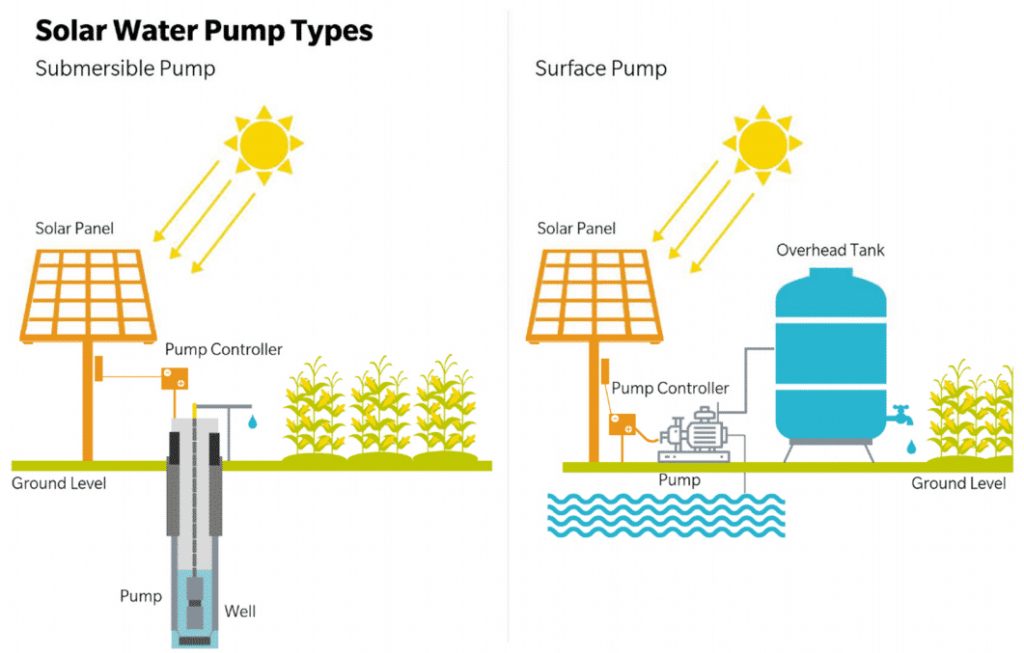
Surface Pumps are typically less expensive than submersible pumps and can draw water from a spring, pond, river, or tank, and push it far uphill and through long pipes to fill a storage tank or to pressurize it for home use or for irrigation, livestock, etc. The pump may be placed at ground level, or suspended in a well in some cases. For trouble free operation, low energy use and 15 year life span we recommend the ATO series solar water pumps.
All pumps are better at pushing than pulling, since the vacuum a pump can draw is limited to atmospheric pressure (about 14 psi). At sea level, a pump can be placed no higher than 10 or 20 feet above the surface of the water source (subtract one foot per 1,000 feet elevation). Most wells are much deeper than this and therefore require a submersible pump, which can push the water up to the surface.
All in all, the main aspect related to the efficiency of a solar water pump is based on three variables including pressure, flow and input power to the pump. Wire-to-water efficiency is the commonly used metric that determines the overall efficiency of a solar water pump (as the ratio between the hydraulic energy that comes out of the pipe and the energy coming over the electrical wires through solar panels).